The whole point of putting effort into blogging is to make money from the comfort of your couch. With over 600 million blogs on the web, it’s nearly impossible to rank all your blogs to make the most money with it. That’s where search engine optimization comes into the picture.
I’ve always been a preacher of value over money. However, you can’t live a life on values. You need money to pay your bills, not values. There’s a thin line of difference between blogging for money and blogging to add value.
This guide is for those who want to learn how to get visibility on search engines so that they can make more money. Again, if you want to read this guide just to make more money, you won’t find anything useful.
What I’m going to share here is the practical experience that has helped me rank my posts, which are in no way profitable in terms of money. Sure, I’m ranking above brands right now, which will compound & compensate with revenue 6-8 months down the line.
Apart from the theory that’s available everywhere on the web (which I’ll talk about in a bit), I’m gonna be sharing my experience of creating content.
With that said, let me share everything I’ve learned about search engine optimization. Please note, this guide is just for those who want to learn about SEO for blogging. The topic is very wide to cover in a single post, so the soul of the post would be to make your blog more visible on search engines so that you can make more money from it.
Understanding how search engines work
Since you’re into blogging search engines will be the primary source of traffic for your blog. Considering this fact, it’s important to understand the working of the primary source of traffic.
A search engine is a too complex piece of software, only 3 components are relevant. The three components are:
- Crawler
- Search index or knowledge base
- Algorithm
These three elements together serve the results you see on the SERPs. Let’s see how these components work in action.
Crawler
The real job of a search engine begins even before you perform a search. The crawler or the web spider continuously crawls all the webpages (new or updated) to find more & more information.
This is like proactively roaming around to learn the ways around a city so that you can take the best & shortest route to reach a destination.
Remember that scene from Sherlock Holmes S01E01, where he tried to figure out the best way to get in front of the cab on foot?

Okay, this is not that scene but you get the point if you’ve watched it.
So yeah, the crawler does the job of crawling all possible pages that are live on the internet. As part of crawling, it tries to understand the content & context of the web page.
It’s important to know that search engines do not understand anything other than the code. Depending on the CMS you have for your blog, you’d be able to see the code that search engines actually can read & understand.
So the bottom line is the crawler keeps scanning the webpages & store the information in the huge database called knowledge base.
That’s the second component.
Knowledge Base
This is simply a database that stores the information about the crawled pages. The only job of the knowledge base is to organize the information based on relevance & similarity of a keyword.
The KB is trained to bunch information about, for example, “keto diet” from different sources together. This is to save time while looking at all the relevant searches when the request is made.
Next time when you make a search on Google, notice the number of results shown. It will be present under the search box as shown below.
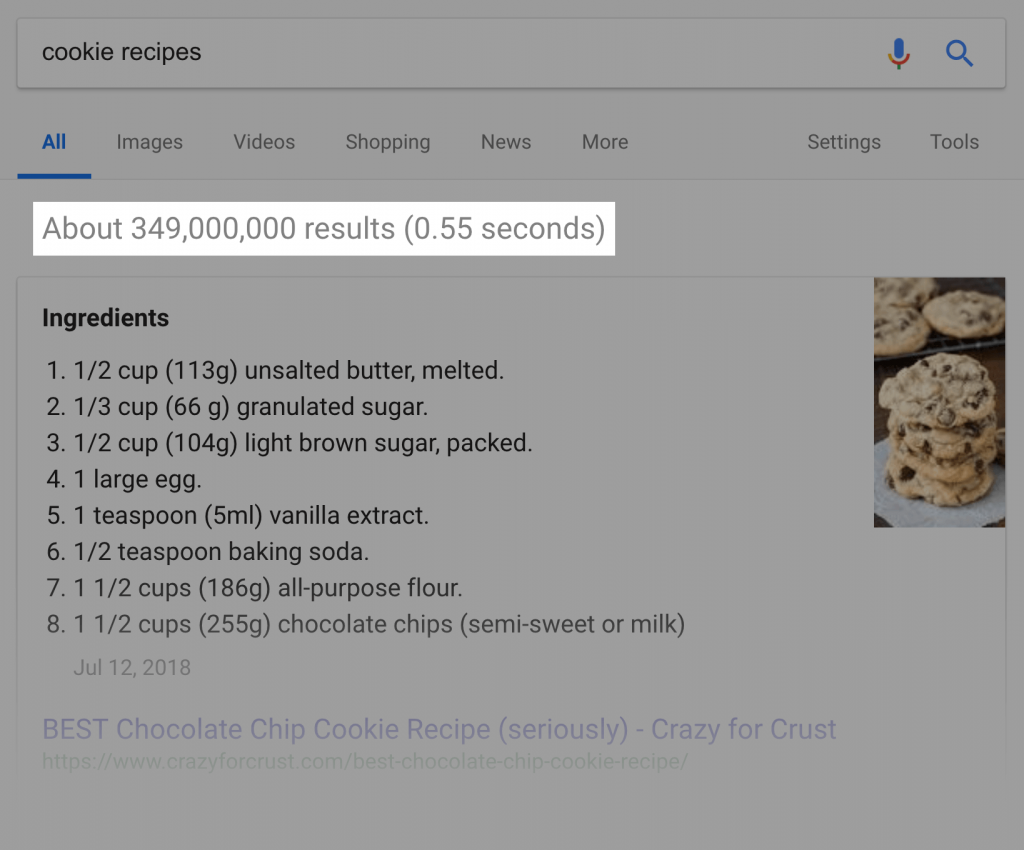
See? Nearly 350 million results on “cookie recipe”. So the only job of the KB is to group all the information related to “cookie recipe” together.
How this is served on the SERPs is something very very much complex and it was done by the most complex element of the search engine.
The mighty search algorithm
The secret sauce of a search engine. Something, everyone is afraid of. The search algorithm is the complex logic that the search engine uses to rank the results served to the end-user.
In the example shown above, 350 million search results have been served. The results that are at the top and the 350 millionth result isn’t random.
The algorithm ranks these results based on 200 plus ranking factors and the algorithm is updated at least twice a day (both major & minor updates). Why it needs these many update is a different story, which can be discussed in a different post.
Though there are over 200+ ranking factors, only a handful of them are primary factors. The remaining fall under the primary ranking factors.
Here are some of the most significant & primary ranking factors on Google.
- A Secure & Accessible Website.
- Page Load Speed (on desktop & mobile)
- Mobile Friendliness.
- Domain Age, URL, & Authority.
- Optimized Content for End Users
- Technical SEO.
- User Experience
- Links (internal links, external links & backlinks)
These are just a handful of ranking factors that influence all other ranking factors. However, if you take care of these, everything will be taken care of.
So this is how the search engines work in a nutshell, there’s a lot of things that run behind the curtains, but this is what that matters the most & you should know about it.
Moving on to the meat of the post.
What is SEO?
SEO stands for search engine optimization. It’s basically a set of best practices that helps you gain more visibility on search engines for various keywords you’re targeting.
As mentioned in the previous section, the crawler scans the information in advance and stores it in the KB. The KB or the search index organizes it depending on the relevant keywords.
When a search is made, the algorithm looks up to the KB for a bunch of organized documents of information relevant to the “search term”.
Just before serving, it ranks the search results based on 200 ranking factors.
This is the process.
Now, SEO is having this process work in favor of you.
I’ve mentioned the most significant ranking factors above. Use those to begin practicing SEO. Implement it on your blog and see the changes it brings.
SEO is simply the best practice that you implement to get in front of more & more people who’re constantly looking for solutions on the web.
Speaking of the number of people, 5.5 billion searches are made every day.
Gaining visibility amidst this huge number of searches made about almost every topic under the sun is not a child’s play. Sure, it’s not difficult too if you get it right.
The end goal of SEO is visibility on search engines. With visibility comes traffic to your blog. There are a lot of other factors that are governed after the user land on your page, but that’s something for a separate post.
Just gaining visibility on search engines doesn’t mean you’ve won. You must retain users on your page once they land on your blog.
How SEO works?
The whole point of SEO is to make the search engine to see your content & show it to the end-users. Your job is to ensure that search engines can see your content and the end-users find it useful.
The more they find your content useful, the higher it will rank. And it stays at the top until it’s helpful. If you don’t have the intention & right mindset to help your target audience with their problems, no amount of effort you put in doing SEO is going to help you.
The intent & need stands at the core of SEO. Your SEO is as effective as your expertise in solving problems faced by end-users.
As part of working, search engines have a ton of awesome features that can be leveraged to take advantage of SEO. Let me shed some light on that here.
Organic vs Paid Search
Organic results
Almost 85% of search results on Google are organic, & less than 15% of results have ads. Organic results are the ones that are naturally ranked by the Google search algorithm without any sponsorship.
These results pass through the scrutiny of the algorithm & are ranked on “merit”. You can’t pay to rank higher, there’s no way that’s becoming a reality.
Even for the paid ads, the ranking is done based on the quality score of the ad copy. In other words, search engines rank the results based on the quality of content & overall experience the end-user is having while on your page.
While the search engines are keeping the three components (crawler, search index & algorithm) busy with serving the search results, there’s another component, the algorithm itself, it keeps an eye on the engagement on the search results.
The algorithm not only ranks the results from the search index but it also dynamically updates the ranks based on the metrics. Probably the toughest job for the algorithm is to dynamically rank the search results in real-time.
Note: When we talk about “SEO”, it simply means ranking for the organic listings. Paid ads are in a separate bucket, which I will be explaining in a bit.
Paid Ads, or Pay per click (PPC)
Since Google has 5.5 billion searches every single day, there are a lot of commercial searches that can be monetized by placing ads along with the organic search results.
This is to better serve the end-users with highly commercial search results & offers for their ‘intent’ of spending real money.
That’s where paid ads come in the picture.
As mentioned above, less than 15% of search results have ads, it becomes clear that there are very few commercial search terms that the search engine can monetize.
The scope of this blog isn’t to run ads, but to make money out of it.
With that in mind, let me tell you how ads can help you make money.
When a publisher opts to run ads on Google’s display network, it includes running the ads on a service called Google Adsense.
Let’s suppose I’m running an ad on Google & choose to run as an image ad. My ads will be displayed on publishers signed up for Google Adsense.
Every time someone clicks on my ad displayed on the publisher’s blog, they get paid a small percentage out of what Google makes.
So there are 3 parties involved in this whole process.
Advertiser: Who wants to get discovered on Google & pays to run their ads on the network.
Publisher: Who has a blog & approved to run ads by Google Adsense.
Google: Who acts as an intermediate who shares the ad spend with the publisher.
Google has paid nearly $10B to the publishers as share.
The only advantage of running ads on the search engine is that it gives you results almost immediately. However, if you wish to continue paying to search engines, be aware that you will get results only till you continue paying.
Furthermore, you will have to continue paying until you become a self-sustaining brand with loyal followers performing a branded search that benefits you.
I can discuss this in ultra detail in a dedicated post in the upcoming weeks. For now, let’s dive into the type of SEO you should be aware of.
Types of SEO
On-Page SEO
The most important element of SEO is on-page SEO. Without this all your efforts are pointless.
So, on-page SEO is a set of best practices you apply to an individual page level. Be it an individual blog page, your sales page, product page, or any page for that matter.
While SEO is a marathon, there are certain things that are in your control. Though there are just a few things that are in your control, they’re powerful enough to help you gain enough traction on the search engines.
On-page SEO, as the name suggests, is everything you do on the individual page so that the search engines can understand the ‘context’ of the page better.
Here are some best practices that can help you get started with on-page SEO:
- Avoid keyword stuffing: Keyword research is still important & will always be. However, you can’t stuff keywords like it was possible a couple of years ago. I’ve used contextual because search engines have started to understand the keyword better. So when the search intent wave is getting higher & higher, context is what bridges the gap of intent. If your content isn’t contextually sound, it’s as good as being in the drafts. Focus on the problem of your target audience, rather than the solution. Remember, they search with the ‘problem’ as the search term, not the solution. So please stop promoting the solution. Research with this in mind.
- Avoid black hat SEO: You will be tempted, approached & convinced to use black hat SEO, but refrain from doing it. Google & other search engines are holding the forts against it & you can’t win in the long run. I will talk about black hat SEO in the subsequent section, but for the sake of this section, black hat SEO is everything that’s against search engine guidelines.
- Avoid thin content: Thin content means articles under 1000 words. Though there are articles under 1000 words ranking well & doing well on search engines, studies have found that articles that are over 2000 words tend to perform well on search engines & social media.
- Avoid duplicate content: As the name suggests, duplicate content that’s available as multiple copies on the web. Be it in the form of repurposed content or plagiarized. Even if you give credits at the end of the post, that still counts as plagiarized. The search engine wants to serve the best search results to its end users, so plagiarized content is definitely not among them. You can use canonicalization to educate search engines about the original source. Search engines freak out when confused, don’t let them freak out.
- Avoid auto-generated content: Only bot search engines love is the crawling bot, everything else is spam for the search engines. Here’s how Google has officially talked about auto-generated content. There are free article spinners available. I have used & tested it personally (only for testing purposes), trust me it doesn’t make any sense. Absolutely nothing.
That was a little bit on what not to do, let me share some things you can do instead.
- Meta tags: Search engines do not understand the text, it only understands the HTML code. Meta tags are the only fragments of grammar search engines can understand. Make use of Meta tags like title tags, heading tags, description tags to give hints about the page. These are the first elements that the search engines read to get started with.
- Internal links: Internal links are one of the highly underrated elements to improve the overall SEO of a site. You can use interlinks to rank newer posts by linking the new posts in the already ranking posts. Interlinking is the art of knitting newer posts in the performing posts to not only enhance the user experience of the end-user but also to boost the traffic. Also, make sure you don’t flood the post with interlinks, there are guidelines laid by Google against this. Even if there weren’t any guidelines, think from the end user’s point of view. You yourself wouldn’t like a lot of interlinks distracting, I don’t like it. I abandon the page instantly.
- User-friendly navigation: Navigation is the most affordable way to direct the crawler to the most important pages of pillar content. I personally add the pillar content in the menu which links to most of the blog posts on this blog. The trick is to serve the pillar content on a silver platter to the crawler so that it can find it’s way to other posts on your blog. Make sure you interlink all the relevant posts in the pillar content.
- Anchor text: Yet another interlinking on-page SEO strategy is anchor text. Anchor text is a title tag you add to the links you embed in your posts. Anchor texts can help the crawler get a glimpse of the post it’s about to crawl. Very powerful on-page SEO strategy & equally easy to implement.
- Redirection: Redirections are fine. There are times you have moved a post to a different URL. However, avoid redirecting a page to more than 3 pages. These are guidelines stated by Google, but I think redirection shouldn’t be more than one. Furthermore, when you redirect a page to a new location, make sure it’s a 301 redirect. 301 is a redirection status code that passes up to 99% link equity.
Off-Page SEO
Everything you do outside of your blog to bring traffic (and hence rank higher on SERPs) is considered as off-page SEO. However you promote, when someone interacts with your post, Google records the engagement & uses that for future use.
Sure, the traffic falls under the referral traffic bucket, but the interaction that happens due to that is considered to rank your webpages on SERPs.
If a blog post linked in a newsletter has engagement like session time, comments & sharing, then this goes to Google as a green flag.
The whole point of off-page SEO is to tap into the existing population on the platform you’re promoting content. By doing that you enable leveraging:
- Backlinks (link building)
- Improve domain authority
- Increase traffic
The soul of off-page SEO is link building. Every step you make towards off-page SEO goes to link building.
The reason why off-page SEO is highly important is that there are a ton of platforms & ways you can promote your content & repurpose to bring your blog.
Here are some awesome ways you can incorporate it to implement off-page SEO:
- Social media marketing: Leverage the power of the ready-made population on social media already consuming huge amounts of content on the platform. SMM is a universe in itself. Take Facebook marketing for example. Facebook has 2.6B active users a month. With such a huge population on the platform, it’s extremely difficult to build a presence there. It takes months of continuous efforts to leave a mark on Facebook, especially when Facebook’s organic reach is officially dead.
- Guest blogging: Though guest blogging is losing it’s a charm, thanks to forums like Quora & Medium. It’s still a great way, competitive & even more extensively fruitful to get traffic, build authority & most importantly, get backlinks. Though a lot of blogs that permit guest blogging do not permit linking to your personal blog posts. Even if they do allow, it’s a no-follow link, which means you won’t get the link juice or the authority that flows to your page(s). That being said, you can still guest blog to build authority & presence which you wouldn’t have if you didn’t guest blog.
- Social bookmarking: Bookmarking sites like Reddit, StumbleUpon & Pinterest has been getting a lot of attention of late. Like every other social platform, it’s important to serve useful information as your attempt to posts on the platform. I’ve not personally used Stumble Upon, but Reddit & Pinterest works purely on value. If you can add value, you will rule the platform.
- Email marketing & Push notification: Email is the #1 marketing channel, at least for me. We check our emails every day at least once, I do it. Emails are the closest you can get to your target audience & once build a decent audience on emails, you can shoot emails every time you publish a blog. You can also have weekly or bi-weekly newsletters that containing all the blog posts published in that duration. Push notification is yet another option to send traffic to your blog by setting up push notification services like Pushengage or Subscribers.
There are other ways that you can use to promote your blog, but these are probably the only ones I’d be doing for the rest of my career unless there’s another benchmarking way. Also, these are enough, to begin with. You can explore other ways that are available, I’ll stick to this since these are working like a charm for me & established bloggers I’m aware of.
Moving on to the part where you will be getting your hands dirty in real technical stuff.
On-Site SEO/Technical SEO
Technical SEO, as the name suggests involves a lot of technicalities. The first two types of SEO are done for humans, this one is exclusively for the search engines.
Everything you do as part of technical SEO, make sense only for search engines & the end users wouldn’t even see throughout their association with your blog.
Technical SEO is all about how well search engines are able to understand your blog & the content on it. Speaking of understanding the blog & its pages, search engines look for identifiers that become the fundamentals of technical SEO.
Technical SEO is mostly a one-time setup for the whole site. For individual pages, the technical part might need your attention every time you create one.
Here are some technical SEO opportunities for your blog:
- Structured data: This is a framework available on all major search engines that help the search engines understand elements on your blog & individual pages. Google is the leading search engine, has laid down official guide & guidelines to help you get started with structured data.
- Sitemaps & robots.txt: Sitemaps is an XML document that the search engines can read. Sitemaps are like RSS feed that gets updated every time you publish or update posts. Treat sitemaps as the entry point of your blog.
- Image optimization: Images are one of the biggest hurdles the browsers have to manage. Heavy images or a huge number of images slow down the page. Optimizers like shortpixel can be of great help to compress the image for faster loading without compromising the quality. You can also incorporate lazy loading to hook the visitors while the images load fully.
- CDNs/Browser caching: CDNs are content delivery networks, which nothing but servers or data centers situated across the globe. If you have CDN enabled for your blog, the network stores the cached version of all the servers across the globe. Whenever there’s a request made, the cached version is sent from the nearest location of your user. Since it’s a cached version & since it’s being sent from the nearest location, the page loading is extremely fast.
- Canonicalization: We’ve already talked about this in the section above. So I won’t deep into this, but I’d say one thing that’s relevant here. The main idea behind canonicalization is to avoid duplicate content being crawled & indexed. Canonical tags are red flags for search engine crawlers.
- AMP framework for your blog: AMP stands for Accelerated Mobile Pages. You can create a mobile-friendly website in a matter of minutes, especially if you are a WordPress user. Learn more about AMP here.
- Responsive design for mobile-first indexing: AMP comes with a downside of lack of themes. However, there are blogs that are having mobile-friendly versions without AMP implemented. That’s complicated if you have a WordPress blog. Even though the themes claim to be mobile-friendly, there’s always a huge amount of chunk on your blog, that won’t be mobile-friendly.
Technical SEO is a very vast subject. Just optimizing your blog for fast loading using tools like Google pagespeed insights will suck a lot of juice of out you & tickle the non-technical bone in you.
So, let me keep it very simple & confine this section with the best practices for technical SEO.
Technical SEO best practices
- Implement hreflang tag for international visitors: hreflang is a tag you add to inform search engine which version of the page to load for which users. Instead of using Google translate, which isn’t that accurate for all languages, why not make each page available for all the languages?
- Avoid broken links or dead links: You & I, hate 404 pages. So does the end-users. Use this free broken-link checker tool by ahrefs to find broken links & fix it. However, if you are a WordPress user, use this plugin that not only shows you the broken links, it also has a feature where you can delete or replace the broken links.
- Optimize for various search engine features: Google has a lot of features that you can leverage depending on your niche. Implementing these for your blog CAN potentially land you in rich snippets. There’s a whole buffet of search gallery to explore & optimize for.
- Audit & validate you XML sitemaps: There are times when XML sitemaps might be broken due to multiple reasons. You can use this auditing tool to regularly check for broken sitemaps. If the sitemaps are broken, how are search engines gonna know about the updates on your blog? That’s why sitemaps checkups are significant.
- No-index tags: When you get rolling with creating blogs, you discover the need for pages that shouldn’t show up on search engines. You can instruct search engines to not index certain pages like webinar sign-up pages or offer pages which you intend to promote. You can also use no-index tags to avoid duplication of content or use canonical tags to let Google know about it.
- No-follow tags: Crawlers enter your blog with a budget. The aim is to help save as much of the budget as possible so that the crawler can spend on your blog posts. You should no-follow all affiliate, forum links & help pages. However, you shouldn’t no-follow all external links, if the page is directly valuable to your blog post, there’s no point in no-following all external links.
Black hat SEO
This is not the subject of this SEO guide, but it’s important to know about this as you might end up doing it without even knowing the adverse effects of it. Black hat SEO is basically disapproved practices laid by search engines. The practices are against the terms & conditions set by search engines by Google, bing & others.
Here are some guidelines laid by Google & Bing that defines approved best practices that will explain it all.
Black hat SEO works literally like black magic. It’s almost instant to produce results & sooner or later it will be caught by search engines and penalized.
So let me share some of the most practiced & recognized black hat SEO techniques.
- Content automation: Content that’s developed by bots & article spinning tools.
- Doorway pages: Pages that rank for certain keywords & then irrelevant redirect to something else. It’s a big no-no from a user experience standpoint.
- Hidden texts or links: Links & HTML text that’s kept hidden is one of the most practiced black hat techniques. This is to increase revenue, redirect to some other page & track unethical elements.
- Cloaking: Cloaking is when you present a different URL to the search engine than to the end-user. That’s literally spamming.
- Irrelevant keywords: Keyword stuffing is still a thing. I’ve seen pages highly stuffed with keywords rank atop. Google algorithm can’t do anything for that since the keyword-stuffed page is the best result the end-user can get. Even though it’s not that bad from a UX standpoint.
You can check out the whole list shared by Google here.
Furthermore, you can report webspam since search engines can’t find all the spam. If you have been attacked by any malicious code, you can submit your blog for malware review after you’ve removed the code. Also, there are times you’d get backlinks spammy websites, you can disavow about this here.
As part of white hat SEO, it’s everything you do, mentioned here in this post & guidelines by search engines.
Creating SEO friendly content like a pro
By creating SEO friendly content, you’re actually helping the search engines understand your content and help decide it’s rank. The trick is to make it as easy as possible.
No matter how non-technical your target audience be, they will still understand a little bit of what you have to say. But search engines will need everything spoon-fed.
Search engines’ job is to rank your content on the SERPs. The whole point of SEO is to apply the best practices on super helpful content.
If your content isn’t helpful, there’s no point in doing SEO. Even if you do it, you won’t be getting any results.
The way search engines are evolving, you can’t expect to rank without addressing the problem your target audience is facing.
I’ve failed forever as a blogger since I didn’t have a set process of creating SEO-friendly content. After testing & observing a lot here’s a process I follow right now.
Creating SEO-friendly content
Step 1: Come up with a topic
Ensure you pick a topic that answers the burning problem of your target audience. This is to get maximum response & engagement.
Step 2: Perform topic research on forums
I dig about the questions asked by people I want to target on forums like Quora, Reddit & Google Trends. It’s a long time since I have stopped researching for keywords. I only research topics, not keywords. This helps me be contextual & target long-tail keywords.
Step 3: Create a great blog post
I’ve always struggled with the introduction part. I sometimes overdid it or did it very poorly. Never perfected it. It’s not perfect even today, but it’s still better.
So I began with the source of inspiration for the post, a gist of the crux of the post.
That’s an introduction. I keep it simple and try to finish the introduction in first fold.
Then comes the main body where I cover topics I’ve found in my research. I also try to include studies & numbers which is one of the easiest ways to get organic backlinks.
Depending on the target audience, I keep the language & topic coverage sensible. There’s no point in over giving value when there are no eligible recipients.
The conclusion is important. That’s where I summarize, leave call to action & guide the users to other relevant posts. Don’t miss that.
Step 4: Edit the post
I prefer fresh mind for editing. Once I’m done with the post, I leave it in the draft & the next morning begins fresh. It’s literally like a new pair of eyes & brain checking out my content.
In the creation mode, I’m in the creator bias where I’ve overlooked a lot of mistakes & compromised on quality. In fact, I’ve got new ideas that I didn’t get otherwise. Interlinks are another aspect that requires fresh mind. That I do in the editing phase.
Step 5: Share & promote
There’s a difference between sharing posts on social media & promoting. It’s repurposing content, i.e literally new set of content for medium, Quora & other social media posts that link back to my content. The idea is to think of as many pieces of content that can have my blog post as interlinks. I call these posts as bypass content because those posts pass through my blog posts.
Step 6: Optimize for impressions
This is the biggest change in my approach. I don’t perform keyword research before publishing blog posts anymore. Maybe this approach is wrong, but it’s working for me. What I do instead is, I let the post get indexed by search engines, and then check the impressions data.
Impressions is a number of times my blog posts have been served in search results irrespective of the rank. That’s exactly what I have to optimize. Once the impressions data flow in, I sprinkle them around the post only if they can be added naturally.
If I can’t, that’s ideal for a new blog post. Easy-peasy.
Since you’re just starting out, I don’t want to guide you to skip the elementary steps of keyword research. Begin with that, only then you will understand the value of topic research.
However, you can & should research with topics in mind.
Keyword/Topic research & search intent
I’ve talked about topic research & keyword research so I won’t speak in that context. However, there’s this element called search intent which making a lot of changes in the search algorithms lately.
Pick any updates that have happened in recent years, including the mighty hummingbird update. All have focused on search intent.
So what exactly is search intent?
Search engines have shifted their focus from the keyword to the meaning, context & intention of the search term.
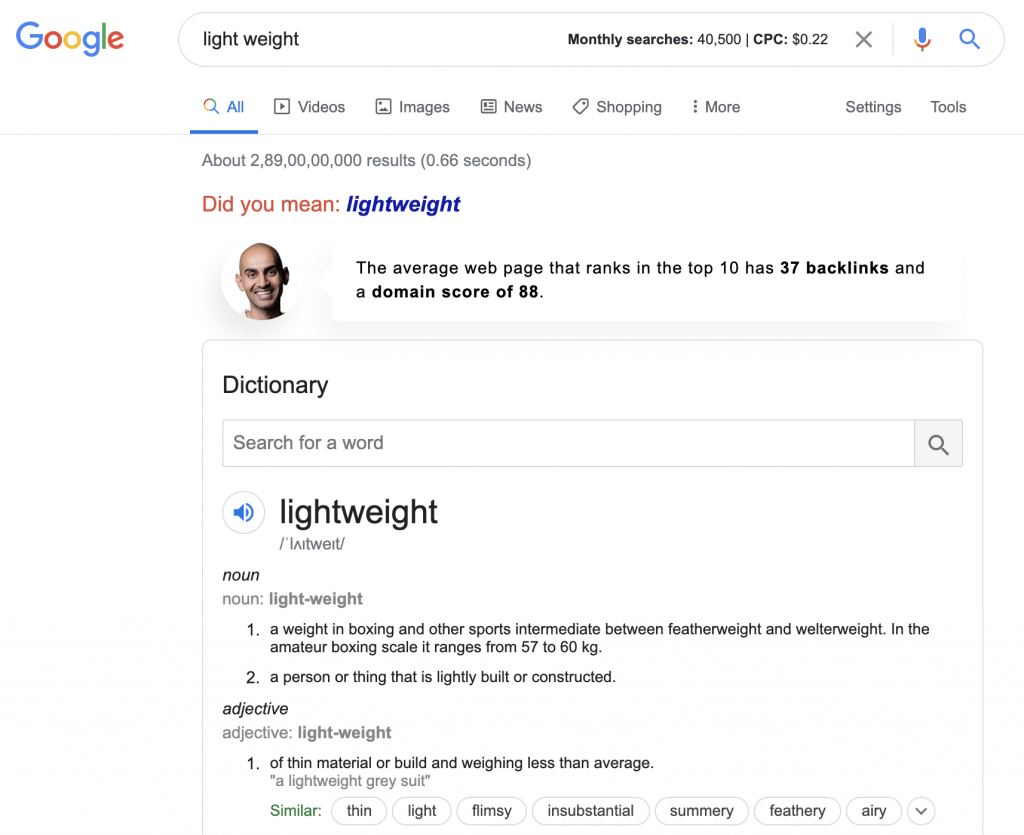
Let’s take an example of this search.
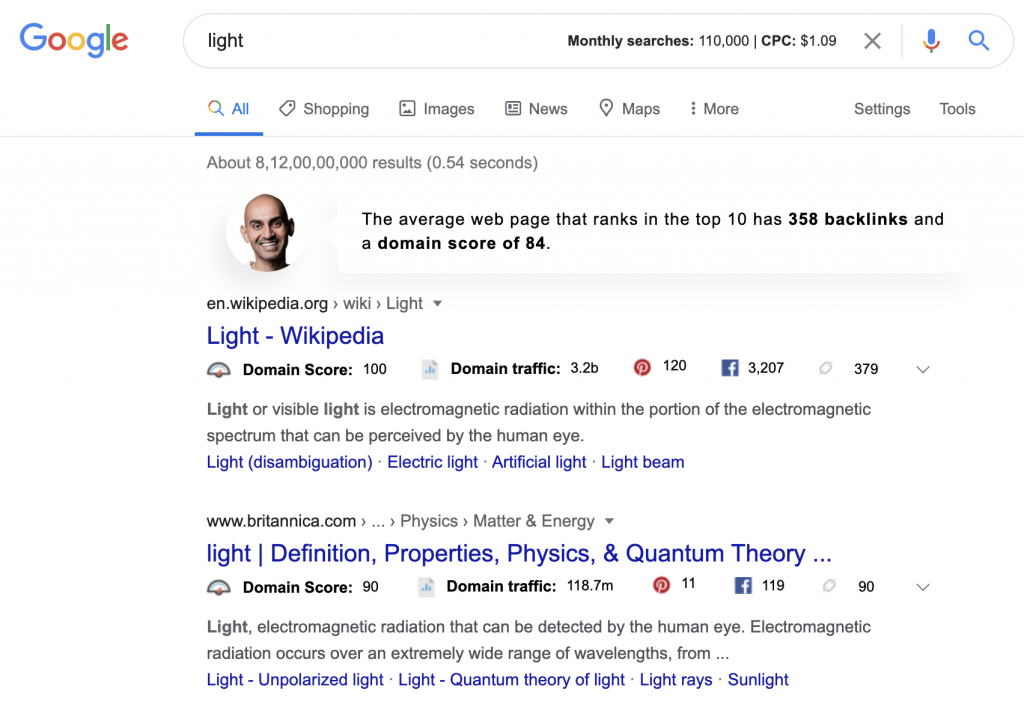
If you take a look at the search results here, you’d find all variations of the possible meanings of the term, ‘light’.
Search engines can’t decipher the intention, so it served all the variations. The light that eliminates darkness, businesses that has ‘Light’ in their business names.
But what if I was looking for light in terms of weight? Search engines wouldn’t understand this intention unless I specify so.
That ‘in terms’ of is the context & search intent.
See how results change & magically become contextual just by searching specifically?
Best SEO Tools (free & paid)
“A craftsman is as good as his tool.”
Here are some tools I use for various purposes of blogging.
- Google trends: I use trends to find trending stories in my target geography. I decide on my URLs of posts based on my research on trends.
- Answer the public: This tool spits out questions people are searching online. Simply enter the target keywords & you will have questions & their variations in a matter of seconds.
- Ubersuggest: I’ve been using this tool since its earliest days. The tool is a miniature version of premium tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz & Serpstat.
- Canva: Create stunning graphics for your blog at absolutely no cost. Though the assets you get for free are limited, its enough to get started with.
- Quora & Reddit: I used it for topic research & repurposing content. It might a platform, but to me, it’s a tool.
- Yoast SEO: A WordPress plugin for creating a custom title for SERPs, managing SEO score at the of writing the post.
- Ahrefs keyword generator: Generate keyword ideas as relevant keyword is an important ingredient for a SEO-friendly post. This free tool can show you 100 keywords related to the seed term you enter.
- Keyworddit: If you’ve got inspired by my idea of using Reddit for topic research, here’s a tool that will help you get keywords in specific subreddits. You just have to enter the name of subreddit & you have access to all the trending keywords in the subreddit.
- Alsoasked.com: This tool fetches questions from People also asked boxes. It can help with topic research without getting tangled in SERPs looking for that.
Here’s an example of what the tool can do:
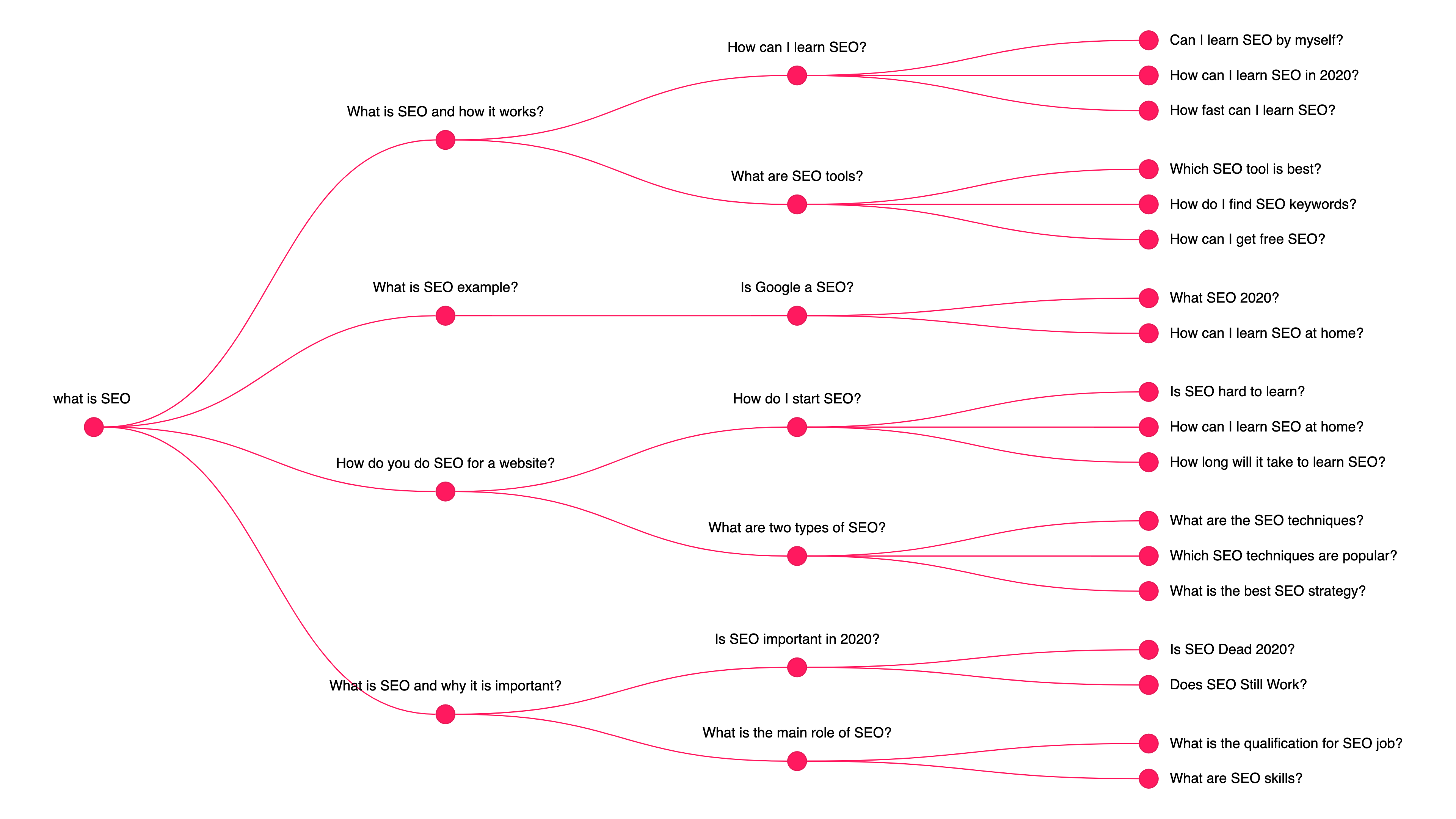
Frequently asked questions for SEO
1) Can you pay Google for SEO?
Nope. Even google doesn’t rank its own content on the SERPs. Google can’t control the search results, it’s ranked by the algorithm which is biased. If not efficient, it’s definitely not biased.
2) How much should you spend on SEO?
Depends on the results you want. SEO is like stocks that pay you a dividend, the more you spend the better.
3) Is SEO easy?
It’s easy if you do the right thing. The right isn’t following guidelines, it’s following the mission statements search engines like Google.
4) Best way/place to learn SEO?
Google it, YouTube it. There are a lot of journals, blogs, & mentors teaching about SEO. But make sure you apply what you’re leaning. The best teacher is the mistakes you commit while implementing the theory part someone else has taught you.
5) How to learn SEO for free?
Same as above. Google & YouTube for sources. Most of the content that ranks on these search engines is free.
6) What are some basic guidelines for SEO?
- Don’t spam
- Produce quality content
- Have user-friendly navigation & design
- Have sharable content
- Implement strong On-Page SEO
- Add value before thinking about money. Build relationships & engagement, the money will follow.
7) What is SEO writing?
It’s simply writing with all the SEO best practices in mind. The practices I’ve been discussing in this post.
8) What is the first step in SEO?
Pick a niche. Start with you know or love to do. If you’re confused with a lot of topics, start working on all of them. Soon you will realize the connection with one topic, move ahead with that.
9) Is SEO necessary?
Unavoidable I’d say. If you want to get visibility among 600+ million blogs, SEO is unavoidable.
10) Is SEO dying in 2020?
Not at all. It’s getting more significant & crucial for online businesses than before.
11) How is SEO different from local SEO?
SEO is done for international prospects & target audience, local SEO is done for ranking in local geography.
12) Can SEO be a career?
Yes. Craig Campbell has survived decades doing SEO for companies. He is an inspiration for many.
13) How to get your blog on Google?
Register on Google search console & submit your sitemap to get started.
Final thoughts
After spending a week on this guide, I’ve reached the conclusion. I myself have learned & updated a lot creating this guide. I’m sure it has helped you understand what exactly SEO & it’s power.
Let me tell you, after doing SEO for almost a decade now, this is just scratch off the surface. SEO is a huge space of opportunity to grow your search traffic & make money online.
I want to be very clear with this guide that SEO is a marathon, it’s not a sprint. If you want to make a quick buck, this method isn’t for you.
With that said, I leave the ball in your court. Let me know your thoughts in the comments below. Share this post on social media & anyone who’d be needing this.

